Introduction
OSHA’s hazard communication program is a cornerstone of workplace safety, particularly in healthcare settings where employees are exposed to a variety of chemical, biological, and physical hazards. Ensuring that healthcare professionals are aware of these hazards and know how to manage them is crucial for maintaining a safe and healthy work environment. This article delves into the importance of hazard communication in healthcare, the essential components of an effective hazard communication program, and best practices for its implementation.
Importance of Hazard Communication
Hazard communication in healthcare is vital for several reasons:
- Employee Safety: Healthcare workers handle hazardous substances such as pharmaceuticals, disinfectants, anesthetic gases, and potentially infectious materials. Proper hazard communication helps employees understand these risks and how to protect themselves.
- Patient Safety: By effectively managing hazardous materials, healthcare facilities can prevent contamination and ensure a safer environment for patients.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with the Occupational Safety and Health Administration’s (OSHA) Hazard Communication Standard (HCS) is mandatory. Adhering to these regulations helps healthcare facilities avoid legal penalties and ensures the safety of both staff and patients.
- Risk Reduction: Effective hazard communication minimizes the risk of accidents and exposures, reducing the incidence of injuries and illnesses among healthcare workers.
Key Components of an Effective Hazard Communication Program
An effective hazard communication program in healthcare should include the following components:
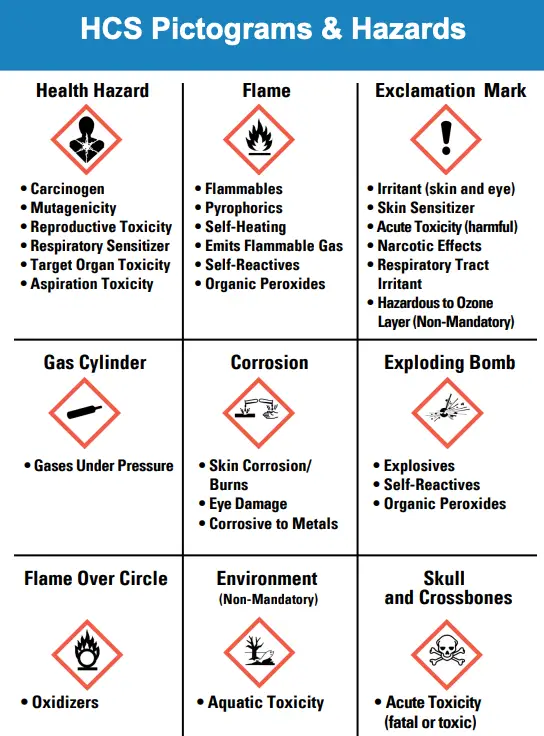
- Hazard Classification:
- Identify and evaluate the hazards associated with each chemical, biological agent, and potentially infectious material used in the healthcare setting.
- Classify hazards based on their potential health effects, such as toxicity, flammability, reactivity, and infectious potential.
- Labeling and Signage:
- Ensure that all hazardous chemicals and materials are properly labeled with the substance’s identity, appropriate hazard warnings, and the manufacturer’s information.
- Use clear and visible signage to indicate areas where hazardous materials are stored or used.
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS):
- Maintain up-to-date Safety Data Sheets for all hazardous substances.
- Ensure that SDSs are readily accessible to all employees during their work shifts.
- Employee Training:
- Provide comprehensive training to all employees on the hazards they may encounter and the proper procedures for handling, storing, and disposing of hazardous materials.
- Conduct regular refresher training sessions to keep employees informed of any changes or new hazards.
- Written Hazard Communication Plan:
- Develop and maintain a written hazard communication plan that outlines the procedures for labeling, SDS management, employee training, and emergency response.
- Ensure that the plan is easily accessible to all employees and is regularly reviewed and updated.
Best Practices for Implementation
Implementing an effective hazard communication program requires a proactive approach and ongoing commitment. Here are some best practices for successful implementation:
- Involve Management and Staff:
- Ensure that both management and staff are committed to hazard communication. Management should lead by example, and staff should be encouraged to actively participate in safety programs.
- Foster a Safety Culture:
- Create a workplace culture that prioritizes safety. Encourage employees to report hazards, near-misses, and incidents without fear of reprisal.
- Recognize and reward safe behavior to reinforce the importance of hazard communication.
- Regular Inspections and Audits:
- Conduct regular inspections and audits to ensure compliance with hazard communication standards.
- Address any identified deficiencies promptly and take corrective actions to prevent recurrence.
- Use Technology:
- Utilize technology to streamline hazard communication processes. Digital SDS management systems and online training modules are examples that can enhance efficiency and accessibility.
- Emergency Preparedness:
- Develop and implement emergency response plans for chemical spills, exposures, and other hazardous incidents.
- Conduct regular drills to ensure that employees are prepared to respond effectively in case of an emergency.
Conclusion
Hazard communication is an essential component of workplace safety in the healthcare industry. By understanding the hazards, properly labeling and storing hazardous materials, maintaining accurate SDSs, and providing comprehensive training, healthcare facilities can protect their employees and ensure a safe environment for both staff and patients. A proactive approach and commitment to fostering a safety culture will help reduce risks and promote the well-being of everyone in the healthcare setting.
Experience Better Healthcare Compliance
We’ve been assisting our clients with their compliance needs for over 30 years. Let our experts help build and maintain your OSHA and/or HIPAA program(s) so you can focus on your patients. Contact us today.